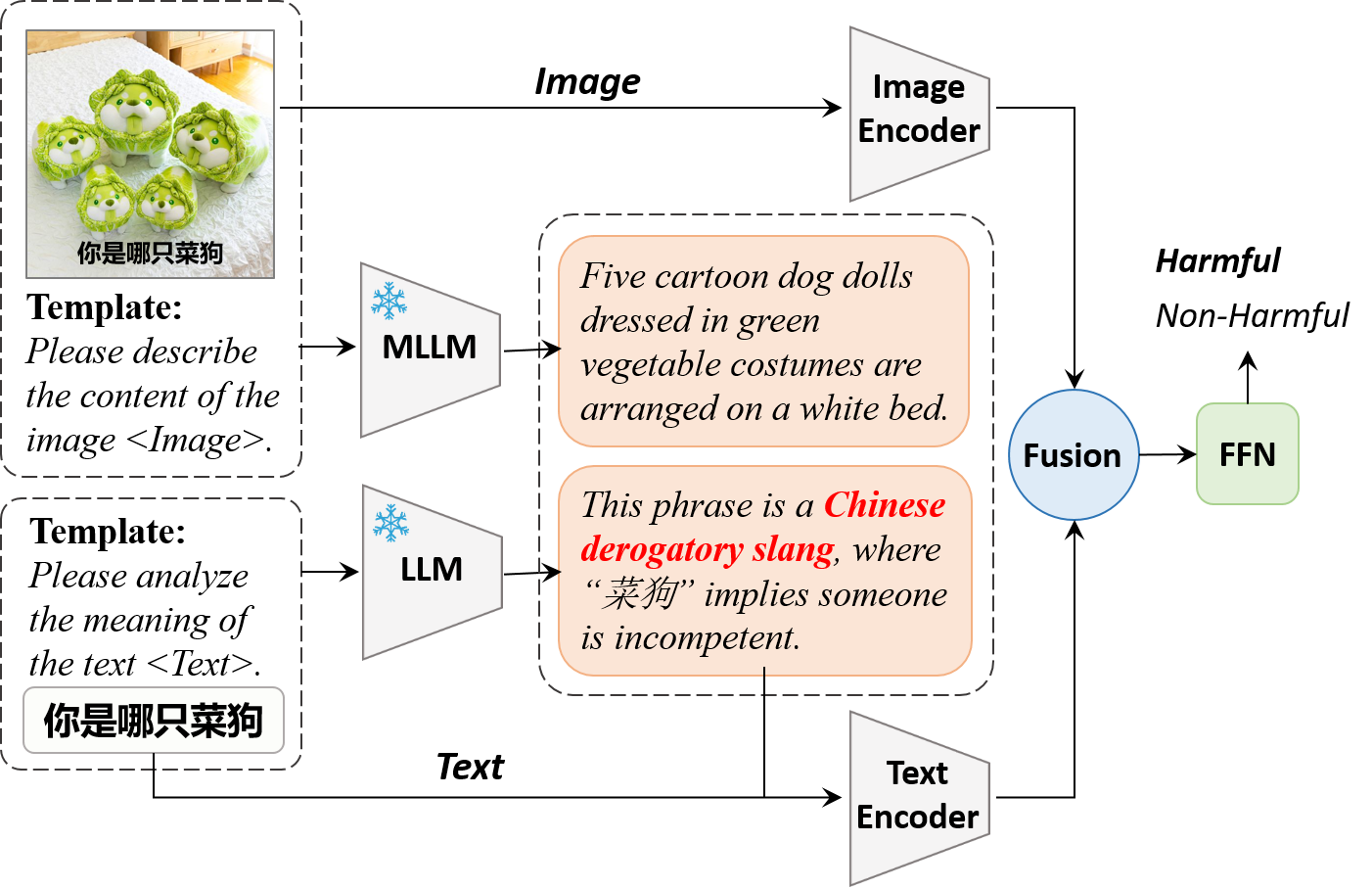
ToxiCN MM
ToxiCN MM contains 12,000 diverse samples collected from Chinese social platforms.
In addition to the basic binary labels (i.e., harmful or non-harmful), we provide fine-grained annotations for harmful memes at two levels of granularity: harmful type and modality combination feature.
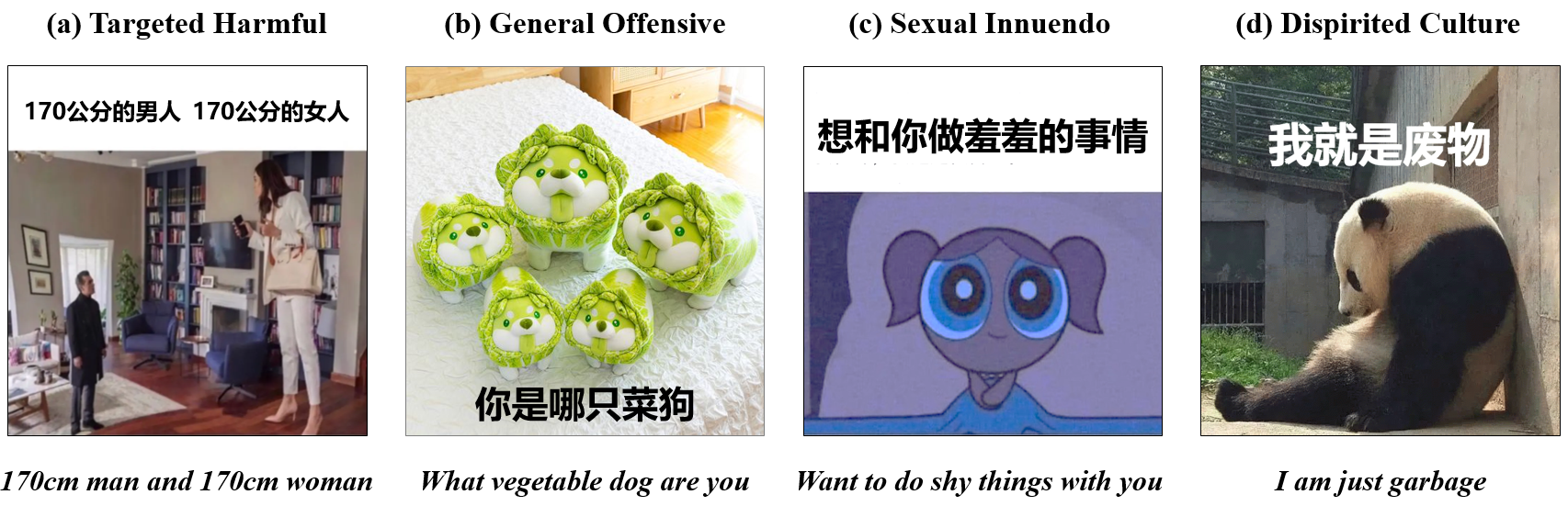
For the harmful type, we focus on both targeted harmful memes and those exhibiting potential toxicity without specific targets, including general offense, sexual innuendo, and dispirited culture.
These memes are identified as the most common harmful types of memes on Chinese platforms based on the consensus of social psychology. Their harm to individuals and society has been widely discussed.
For the modality combination feature, we examine how harmful memes convey toxicity through the interplay of textual and visual elements, either combined or independently, including text-image fusion, harmful text, and harmful image.